Summary
The rise of AI has reshaped global dynamics, emerging as a potent force for individuals, groups, and institutions alike. Amidst its disruptive potential, AI offers transformative solutions, particularly within the judicial sector, where fairness and trust are paramount. However, challenges such as massive case backlogs, inconsistent judgments, and structural complexities persist. Generative AI holds promise in addressing these challenges by expediting case processing, streamlining decision-making, and fostering transparency. By leveraging AI, the judiciary can enhance efficiency, expedite justice, and bolster public trust. Nevertheless, concerns regarding fairness, competency, and accessibility remain, highlighting the need for continuous innovation and reform. Through embracing Generative AI, the judiciary can navigate towards a future where justice is swift, equitable, and accessible to all.
Reference link : Leveraging AI to reduce judicial backlog, fast-track cases
Hashtags : #ArtificialIntelligence #DigitalTransformation #JusticeDeliveryExperience #LegalJourney #GenerativeAI #LegalExperience #AIinJustice #JudicialTransformation #JusticeThroughAI #FairnessInLaw #TrustInJudiciary #AIForJustice #LegalTech #GenerativeAIJustice #JudicialReform #TechForJustice #EquitableJustice
Key Issues in the Judicial System
Huge pendency of cases in courts
India faces a staggering backlog of court cases, making it the country with the highest number of pending cases globally. According to a 2018 Niti Aayog strategy paper, clearing this backlog would require more than 324 years. The sheer volume of cases—over 50 million (5 crores)—across all levels of the judicial system contributes to this challenge. Remarkably, 169,000 cases have been pending for over 30 years in district and high courts. District courts bear the brunt, with 85% of the total cases (4.3 crore out of 5 crore) awaiting resolution as of December 2022. Interestingly, the government itself is the largest litigant, sponsoring 50% of the pending cases. Among the various types of disputes, land and property cases dominate, accounting for approximately 66% of all civil cases. Additionally, 25% of the cases decided by the Supreme Court involve land-related matters.
Insufficient quality time for case assessment & file readiness
Substantial time is needed to study the new case, analyzing the different situations, accused & witness statements, collecting evidence & artifacts, etc. Preparing probing questionnaires, foreseeing the hidden aspect of case & individuals involved, conducting legal research, connecting dots, etc. Preparing a checklist including tasklist & TODOs, alerts & reminders. Etc.
Inconsistency in judgments across different courts for same case
The divergence in judgments between lower courts and higher courts poses a significant challenge within the Indian judicial system. While top-order courts deliver decisions that may differ substantially from those of lower courts, this inconsistency has eroded trust in the system. Occasionally, the judiciary’s decisions evoke pride among Indian citizens, but at other times, biases become evident in their judgments.
Hierarchical structure of judicial system
Indian judicial system does not have very fatty hierarchy, just 3 layers based on our federal governance structure i.e. Supreme Court of India (country level) > High Courts (state level) > District Courts (Civil matters) | Sessions Courts (Criminal matters). Apart from lower courts (district & session courts) there are some special courts as well e.g. Magistrate Courts, Family Courts, Special Courts.
The primary objective of understanding this hierarchy is to recognize that innocent individuals, even in lower courts, often face significant delays. For them, this hierarchy may resemble a long tunnel, with a faint ray of hope visible at the other end.
Need of auto-pilot mode in justice delivery (Proactive instead of Reactive)
The pursuit of justice hinges on uncovering the complete truth. I firmly believe in the adage that “no one can hide the truth and honesty.” However, when powerful entities manipulate the narrative, truth can be buried deep in the shadows.
In such situations, honest individuals may feel disheartened, while those on the wrong side of justice often amplify falsehoods, presenting lies as truth. Yet, I consider this a myth—a temporary distortion. Ultimately, truth prevails, even if it takes years, generations, or sacrifices innocent lives. The delay in justice and the toll it exacts on the innocent are profoundly unfair, yet society bears this cost in the pursuit of justice.
Core Objectives of Justice:
- Protection of Innocents: Justice exists to shield the innocent from harm, ensuring their rights and dignity.
- Empowerment: It should empower those who lack financial resources, leveling the playing field.
- Simplicity and Accessibility: The justice process should be straightforward, especially for those without influence.
- Implicit Justice: Beyond the legal system, justice should permeate the entire government ecosystem.
Call for Auto-Pilot Mode:
- Our judicial system should operate like an auto-pilot—proactive and self-correcting.
- Every step in the judicial process should resound with truth, automatically exposing hidden agendas.
- However, we must ask ourselves: Is our system truly strong and self-sufficient for the poor and innocent? We have much ground to cover on this journey toward justice.
Intentional manipulation in the Judicial System : a cause of concern
Growing up, many of us hold the judicial system in high regard, regardless of whether we agree with specific judgments. However, there exists a fear that speaking out or criticizing a court decision could be construed as contempt of court, discouraging open discourse.
While this fear is one aspect, a more significant concern arises when judges and lawyers intentionally manipulate the law. Some legal professionals, instead of upholding justice, exploit legal loopholes to favor the wrong side. They navigate the legal process ostensibly within the bounds of the law, but their true allegiance lies with those who flout justice.
Competency issue with lawyers or judges
One can witness the court campus of any level, thousands of lawyers can be found with their setup. Very few are competent and stand with justice, while many of them are incapable and they are able to trap clients with careless attitude towards them. I have a dilemma on [incompetency] and that is firstly there should be [no place for incompetent lawyers & judges], secondly [incompetency] should become the [no blocker in the process of justice delivery].
If [incompetency] is stopping the judicial system from delivering justice, then the judicial system does not have [self-consciousness & self-healing] in its DNA. In the absence of the implicit nature of [self-consciousness & self-healing], the judicial system will be under suspicion for poor & innocent people.
I would welcome other thoughts also. To me, the analogy is that a politician without great academic education can also be a great leader, because they always have a good intent of servicing the public, similarly [incompetent] lawyers & judges irrespective of bad & good intent, should be working in established [justice framework] having auto & implicit nature of [self-consciousness & self-healing], which will force every judicial system to deliver the justice.
Unmasking some of the Ironies: Reflections from past
In the labyrinth of India’s judicial history, paradoxes abound—tales that echo both resilience and despair. Here, we unravel some poignant ironies
- A man languished in prison for thirty years, accused of murder. Yet, when the court weighed the evidence, it crumbled like ancient parchment. Acquittal followed, but the scars remain—three decades lost to the abyss of uncertainty.
- Picture an educationist, disabled and resolute. For over a decade, he faced alone all the tides of injustice. The court declared him innocent, but time had already exacted its toll. The scales of justice, at times, tip with cruel indifference.
- The night was ink-black, and a 19-year-old Dalit girl’s life hung in the balance. Brutally gang-raped by those who wielded power, her body was consigned to flames without family consent. The world watched, hearts heavy with rage and sorrow.
- In the shadow of another city of largest state, a 17-year-old girl’s innocence was shattered after she was gang-raped by powerful MLA & members of his team. Those people draped in impunity, left scars on her that time cannot erase. The whole world watched how the system worked in her case.
- Lack of awareness in people about police & judiciary systems. Rather both create fear instead of giving confidence.
- There are many cases where trials have not yet started. Many people could not come out of jail, because no-one belongs to them to take their bail.
- While lodging FIR, it is said that IPC codes are not rightly marked knowingly or unknowingly. This makes the case weak or strong depending upon whether the accused is influential or innocent.
- Many-times, it looks like the justice system is not affordable at all for poor citizens.
AI enabled Judicial System
The Indian judicial system faces significant challenges such as mounting case backlogs, delays in justice delivery, and the need for transparency. In this context, Generative AI emerges as a powerful tool that can revolutionize the legal landscape. By harnessing the capabilities of artificial intelligence, we can address critical pain points and enhance the efficiency of our courts.
Leveraging AI for key issue resolution
Tackling Backlogs
Generative AI algorithms can process vast amounts of legal data, including case law, precedents, and statutes. By automating legal research, these algorithms can assist judges and lawyers in identifying relevant information swiftly. Moreover, AI-driven predictive models can prioritize cases based on urgency, complexity, and other factors, allowing courts to allocate resources effectively.
Fast-Tracking Critical Cases
Certain cases demand expedited resolution—whether it’s a matter of social justice, heinous crime, public interest, human rights, or government service. Generative AI can streamline these fast-track cases by automating routine tasks, minimizing paperwork, and accelerating the legal process. Judges can focus on core issues, leading to quicker outcomes.
Enhancing Decision-Making
While judgments have legal binding, justice transcends mere legality. Generative AI can provide a holistic perspective by analyzing not only legal aspects but also social, economic, and ethical dimensions. By considering the complete context, judges can arrive at more equitable decisions, ensuring justice prevails.
Fairness & Transparency and Trust in the System
Generative AI promotes transparency by making legal reasoning more accessible. Natural language processing (NLP) models can summarize complex legal texts, making them comprehensible to litigants and the public. Public faith in the judiciary is essential. Generative AI will act as a judicial assistant to judges & lawyers and provide relevant & authenticated information unbiasedly with the [reference of source]. AI models would be trained using authenticated information, so AI-powered tools can flag potential biases, ensuring fairness in legal proceedings, so further less chances for requested information, suggestion & recommendation, being the fake information. When citizens perceive a fair and efficient system, their trust in the judiciary grows, reinforcing the rule of law.
In this era of technological advancements, leveraging Generative AI holds immense promise for redefining the justice delivery experience. By embracing these innovations, we can create a judicial system that is not only efficient but also just, accessible, and responsive to the needs of our society. As we navigate this transformative journey, let us envision a future where justice is not delayed but delivered swiftly, where faith in the system is unwavering, and where Generative AI becomes an indispensable ally in our pursuit of a more equitable society.
Analogy of judicial system
Since I come from a software background and have played a role as an [enterprise architect] in several [large, complex & long] projects for the last 15-20 years. I have architected many [large, complex & long] projects to support hundreds of millions of customers and multi-million transactions on hourly basis. As an [enterprise architect], one must ensure that system is safe & secure to avoid any misuse or hack by any wicked hacker, one must ensure that system is stable & scalable in case of unpredicted situation of high load like new year, diwali, christmas or eid, one must ensure that system is resilient or self-healable to stand-up again in case of any planned or unplanned damage.
AI Law Model (Intelligent-Judicial-Assistant (IJA))
[AI Law Model] is the core component which will be trained like a college graduate of law faculty and like a judge taking experience in its judicial service by hearing cases and giving justice on them.
Version 1 (Trained like an academic student)

Version 2 (Trained like an experience judge)

Let’s understand the end-to-end perspective of justice process
Understanding phases of justice process
Justice process in Indian [judicial system] can be divided into 3 phases
| Phase | Major process | Purpose & description |
| Pre-Litigation phase | First Information Report (FIR) | The process begins with the filing of an FIR. When a crime is reported, the police record the details in an FIR. It serves as the foundation for legal proceedings. |
| Investigation | During this phase, the police collect evidence, interview witnesses, and gather relevant facts. The investigation aims to establish the truth and identify the accused. | |
| Litigation phase | Filing of the Case | After the FIR, the complainant or the aggrieved party files a case in the appropriate court. The trial begins, and both parties present their arguments and evidence. |
| Trial and Adjudication | The court evaluates the evidence, listens to the lawyers’ arguments, and considers legal points. Witnesses testify, documents are examined, and expert opinions are presented. | |
| Judgment | Once the trial is complete, the court delivers its judgment. The judgment states the court’s decision, reasoning, and the relief granted or denied. It may award damages, issue injunctions, or provide other forms of relief based on the merits of the case. | |
| Post-Litigation phase | Appeal | If either party is dissatisfied with the judgment, they can appeal to a higher court. |
| Execution | Post-trial proceedings include the execution of the judgment and any further legal actions. |
Understanding the regular litigation process
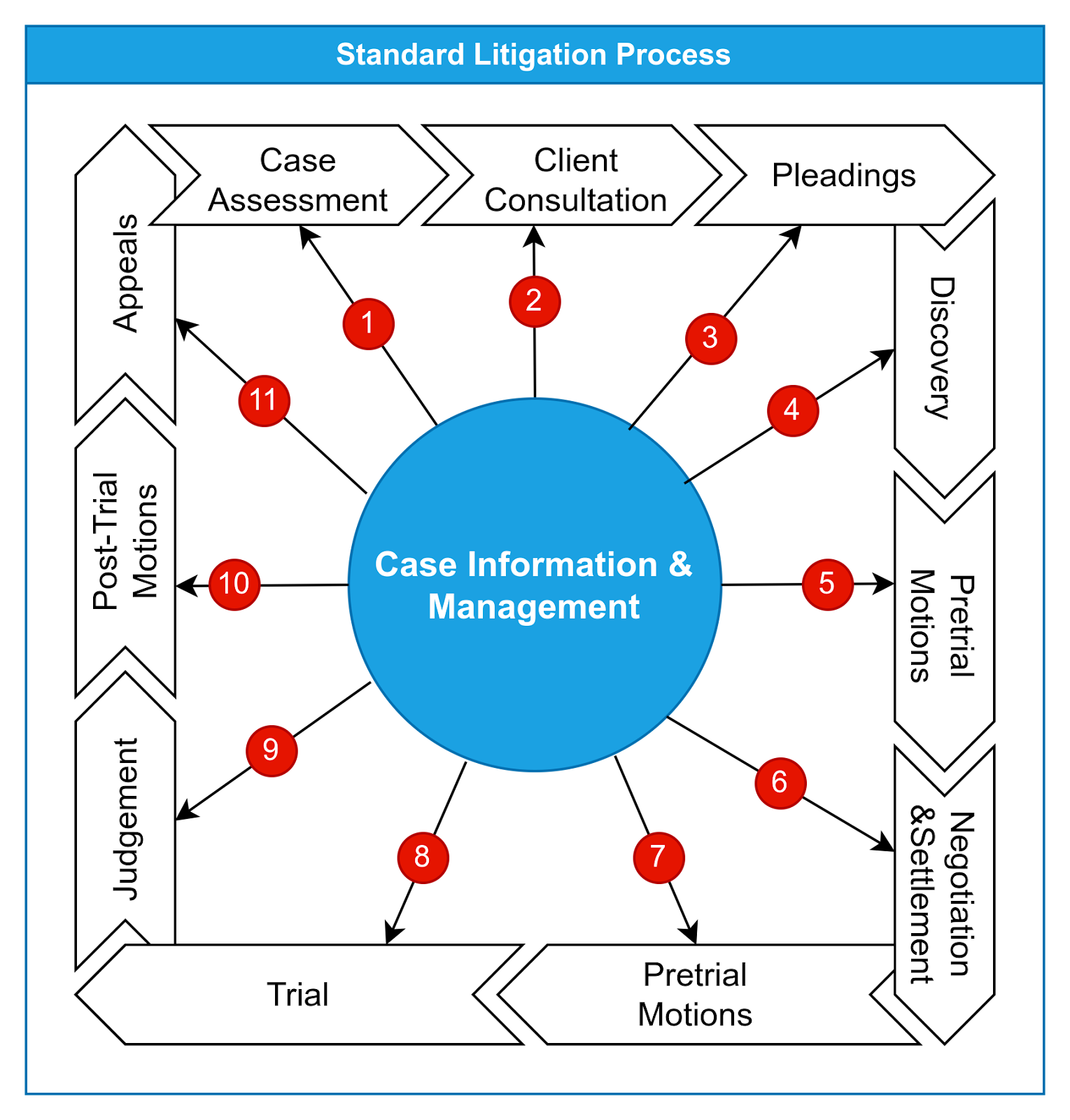
| Case Life-cycle stages | Description |
| Case Assessment | The lawyer begins by assessing the merits of the case, including reviewing relevant documents, conducting legal research, and analyzing the applicable laws and precedents. This helps the lawyer understand the strengths and weaknesses of the case and formulate a strategy. |
| Client Consultation | The lawyer meets with the client to discuss the details of the case, gather relevant information, and understand the client’s goals and preferences. This consultation helps the lawyer develop a tailored approach to representing the client’s interests. |
| Pleadings | The lawyer prepares and files the necessary legal documents to initiate the litigation process. This may include drafting a complaint (in civil cases) or information (in criminal cases), as well as other pleadings such as motions, petitions, or answers to counterclaims. |
| Discovery | Discovery is the process of gathering evidence and information relevant to the case. This may involve conducting depositions, issuing subpoenas for documents or witness testimony, and exchanging relevant information with the opposing party through interrogatories or requests for production of documents. |
| Pretrial Motions | The lawyer may file pretrial motions to address procedural issues, such as motions to dismiss, motions for summary judgment, or motions to suppress evidence. These motions seek to resolve legal issues or narrow the scope of the case before trial. |
| Negotiation and Settlement | Throughout the litigation process, the lawyer may engage in negotiations with the opposing party to explore the possibility of reaching a settlement. Settlement negotiations aim to resolve the dispute outside of court and avoid the time and expense of a trial. |
| Trial Preparation | If the case proceeds to trial, the lawyer prepares extensively by gathering and organizing evidence, identifying and preparing witnesses, and developing a trial strategy. This may involve conducting mock trials, preparing exhibits and visual aids, and anticipating and addressing potential challenges. |
| Trial | During the trial, the lawyer presents the case to the judge or jury, examines witnesses, introduces evidence, and argues legal points. The lawyer advocates vigorously for their client’s interests and endeavors to persuade the trier of fact to rule in favor of their client. |
| Post-Trial Motions | After the trial, the lawyer may file post-trial motions, such as motions for judgment notwithstanding the verdict or motions for a new trial, to challenge the outcome of the trial or address any legal errors. |
| Appeals | If the client is dissatisfied with the outcome of the trial, the lawyer may file an appeal to a higher court. The appellate process involves reviewing the trial court’s decision for errors of law or procedure and presenting arguments to the appellate court for reversal or modification of the decision. |
Now let’s understand various issue resolution by [AI Law Model]
Assistance in Pre-Litigation process (FIR registration)
FIR process is the first step of the judicial system, where FIR report in predefined format is prepared (Please refer to the sample format). Good quality information in the FIR report will always enable the right direction throughout the case execution and judgment in the end. Offense information and incident information by complainants in the FIR report, are the most important sections which should be captured clearly and carefully. Some enhancements as explained below can make the system fair & transparent.
Sample of FIR report
| Police Station…………….. District ……………………. Personal details of the Complainant / Informant: NameFather’s / Husband’s Name Address Phone number & FaxEmail: Place of Occurrence: Distance from the police station Direction from the police station Date and Hour of Occurrence: Offense: Nature of the offence (e.g. murder, theft, rape, etc.) Section (To be decided/written by Office only ) Particulars of the property (in case one has got stolen): Description of the accused: Details of witnesses (if any)Complaint: Briefly lay down the facts regarding the incident reported in an accurate way. Note: At the end of the complaint, the complainant’s/informant’s signature or thumb impression should be there. |
Enhancement # 1 : Incident report by complainant can be enhanced to audio & video recording. [AI Law Model] will automatically prepare the [Incident report] in textual format & desired format.
Enhancement # 2 : To increase public trust and make the process more transparent, [application law sections] & [Nature of offense] will be auto recommended based on [Incident report] analysis by [AI Law Model].
Assistance in Litigation process
| Benefits in different processes | Description |
| Automated Legal Research | [AI Law Model] can revolutionize legal research by rapidly scanning, analyzing, and summarizing vast volumes of legal texts, precedents, and relevant case law. It can assist lawyers in finding relevant legal arguments, identifying case law, and understanding complex legal concepts. |
| Document Review and Discovery | [AI Law Model] can review and categorize large volumes of documents, contracts, and evidence. Natural Language Processing (NLP) helps extract relevant information, saving time and reducing human error. |
| Predictive Analytics | [AI Law Model] can predict case outcomes based on historical data and patterns. Lawyers can make informed decisions about case strategy, settlement, or trial based on these predictions. |
| Contract Analysis | [AI Law Model] can analyze contracts, identify clauses, and assess risks. This is particularly useful in commercial litigation and contract disputes. |
| Transcription Services | AI-powered transcription tools can transcribe court proceedings accurately and efficiently. This improves transparency, accessibility, and record-keeping. |
| Legal Writing Assistance | AI can help draft legal documents, including pleadings, motions, and briefs. Sametime human input is still necessary for the final draft, AI accelerates the process. |
| Case Management and Workflow Optimization | [AI Law Model] can streamline administrative tasks, manage deadlines, and track case progress. It enhances efficiency and reduces administrative burden |
| Sentiment Analysis | [AI Law Model] can analyze emotions and sentiments expressed in legal texts, helping lawyers understand the context and tone of communications. |
Challenges
However, [AI Law Model] brings lots of resolutions to speed-up the justice process and make that fair & transparent too. It’s still essential to exercise with following caution:
- Bias: AI systems can inherit biases from training data, affecting decision-making.
- Ethical Considerations: Legal professionals, who play foul, can misuse AI against ethical practices and human rights.
- Human Judgment: While AI assists, final decisions should remain with judges and lawyers2.
Conclusion
In summary, AI can be a powerful ally in the litigation process, but it should complement human expertise rather than replace it. AI tools can automate legal research, streamline document review, predict case outcomes, and optimize workflows. However, legal decisions involve complex nuances, ethical considerations, and human judgment that AI alone cannot fully grasp. Therefore, a collaborative approach, where AI assists legal professionals, ensures a balance between efficiency and the preservation of legal principles.
References
General
- Pendency of court cases in India
- ChatGPT for drafting
E-Courts (India) Mission Mode Project
- Vision & Objectives (Link)
- E-Courts-Mission-Mode-Project (Link)
- E-Courts-Case Management (CIS 3.0) (Link)
- E-Courts National Judicial data grid (NJDG), [Database of entire judicial case data] (Link)
- E-Courts User Manuals (Link)
About author
Profile : Rajesh Verma – Brief profile
Source : link for this article here
Series : S2 (Artificial Intelligence)
Episode : [S2-AIGAI] Leveraging Generative AI to reduce judicial backlog, fast-track cases,
Author’s approach : Rajesh wants to share his learning & experience gained throughout his career from various sources. Author started the series on architectural topics including AI/ML & GAI topics and this article is one of the episodes in that attempt. Author feels that lots of information is available on various forums, but scattered here & there. Episodes in this series will be designed for most of the relevant topics in architecture-&-design, published gradually and organized in logical sequence. Principally episodes will have linkage with other episodes, so that readers can have proper connection among the topics and would be able to correlate with ongoing activities in their software life. Topics for example will be related to functional architecture, integration architecture, deployment architecture, microscopic view of mostly architecture-building-blocks (ABBs), security guidelines & approach to comply, performance KPIs & engineering, git branch & DevOps enabled automation strategy, NFR aspects (e.g. scalability, high-availability, stability, resiliency, etc.), commonly used architecture styles & design patterns, cloudification approaches, multi-tenancy approach, data migration, channel-cutover & rollout strategy, process standardization & simplification, greenfield rollout & brownfield transformation journeys, etc.
Thank you for reading the post, please stay connected.
No responses yet